Composite materials have become ideal materials for the manufacture of low-altitude aircraft because of their lightweight, high strength, corrosion resistance and plasticity.In this era of low-altitude economy that pursues efficiency, battery life and environmental protection, the use of composite materials not only affects the performance and safety of aircraft, but also is the key to promoting the development of the entire industry.
Carbon fiber composite material
Because of its lightweight, high strength, corrosion resistance and other characteristics, carbon fiber has become an ideal material for the manufacture of low-altitude aircraft.It can not only reduce the weight of aircraft, but also improve performance and economic benefits, and become an effective substitute for traditional metal materials.More than 90% of the composite materials in skycars are carbon fiber, and the remaining about 10% are glass fiber.In eVTOL aircraft, carbon fiber is widely used in structural components and propulsion systems, accounting for about 75-80%, while internal applications such as beams and seat structures account for 12-14%, and battery systems and avionics equipment account for 8-12%.
Fiberglass composite material
Fiberglass reinforced plastic (GFRP), with its corrosion resistance, high and low temperature resistance, radiation resistance, flame retardant and anti-aging characteristics, plays an important role in the manufacture of low-altitude aircraft such as drones.The application of this material helps to reduce the weight of the aircraft, increase the payload, save energy, and achieve a beautiful exterior design.Therefore, GFRP has become one of the key materials in the low-altitude economy.
In the production process of low-altitude aircraft, fiberglass cloth is widely used in the manufacture of key structural components such as airframes, wings, and tails.Its lightweight characteristics help to improve the cruise efficiency of the aircraft and provide stronger structural strength and stability.
For components that require excellent wave permeability, such as radomes and fairings, fiberglass composite materials are usually used.For example, the high-altitude long-range UAV and the US Air Force’s RQ-4 “Global Hawk” uav use carbon fiber composite materials for their wings, tail, engine compartment and rear fuselage, while the radome and fairing are made of fiberglass composite materials to ensure clear signal transmission.
Fiberglass cloth can be used to make aircraft fairings and windows, which not only enhances the appearance and beauty of the aircraft, but also enhances the comfort of the ride.Similarly, in satellite design, glass fiber cloth can also be used to build the outer surface structure of solar panels and antennas, thereby improving the appearance and functional reliability of satellites.
Aramid fiber composite material
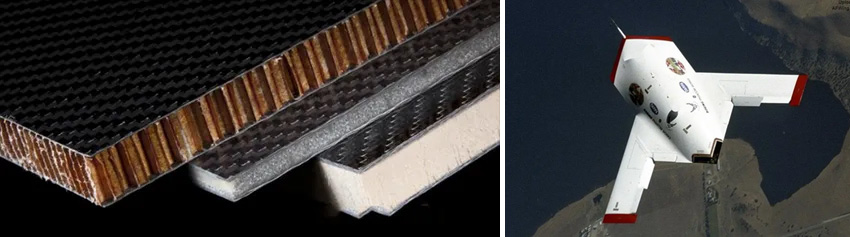
The aramid paper honeycomb core material designed with the hexagonal structure of a bionic natural honeycomb is highly respected for its excellent specific strength, specific stiffness and structural stability.In addition, this material also has good sound insulation, heat insulation and flame retardant properties, and the smoke and toxicity generated during combustion are very low. These characteristics make it occupy a place in the high-end applications of aerospace and high-speed means of transportation.
Although the cost of aramid paper honeycomb core material is higher, it is often selected as a key lightweight material for high-end equipment such as aircraft, missiles, and satellites, especially in the manufacture of structural components that require broadband wave permeability and high rigidity.
Lightweight benefits
As a key fuselage structure material, aramid paper plays a vital role in major low-altitude economical aircraft such as eVTOL, especially as a carbon fiber honeycomb sandwich layer.
In the field of unmanned aerial vehicles, Nomex honeycomb material (aramid paper) is also widely used, it is used in the fuselage shell, wing skin and leading edge and other parts.
Other sandwich composite materials
Low-altitude aircraft, such as unmanned aerial vehicles, in addition to using reinforced materials such as carbon fiber, glass fiber and aramid fiber in the manufacturing process, sandwich structural materials such as honeycomb, film, foam plastic and foam glue are also widely used.
In the selection of sandwich materials, commonly used are honeycomb sandwich (such as paper honeycomb, Nomex honeycomb, etc.), wooden sandwich (such as birch, paulownia, pine, basswood, etc.) and foam sandwich (such as polyurethane, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene foam, etc.).
The foam sandwich structure has been widely used in the structure of UAV airframes because of its waterproof and floating characteristics and the technological advantages of being able to fill the cavities of the internal structure of the wing and tail wing as a whole.
When designing low-speed UAVs, honeycomb sandwich structures are usually used for parts with low strength requirements, regular shapes, large curved surfaces and easy to lay out, such as front wing stabilizing surfaces, vertical tail stabilizing surfaces, wing stabilizing surfaces, etc.For parts with complex shapes and small curved surfaces, such as elevator surfaces, rudder surfaces, aileron rudder surfaces, etc., foam sandwich structures are preferred.For sandwich structures that require higher strength, wooden sandwich structures may be selected.For those parts that require both high strength and high stiffness, such as fuselage skin, T-beam, L-beam, etc., the laminate structure is usually used.The manufacture of these components requires preforming, and according to the required in-plane stiffness, bending strength, torsional stiffness and strength requirements, select the appropriate reinforced fiber, matrix material, fiber content and laminate, and design different laying angles, layers and layering sequence, and cure through different heating temperatures and pressurization pressures.
Post time: Nov-22-2024