Basalt Rebar
Product Description
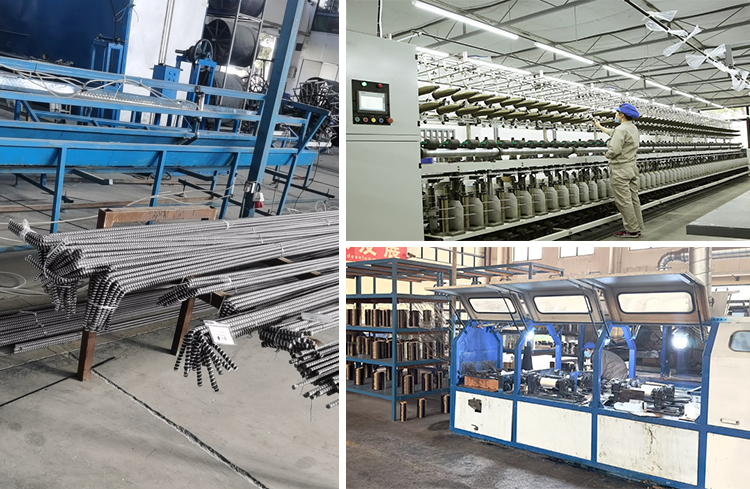
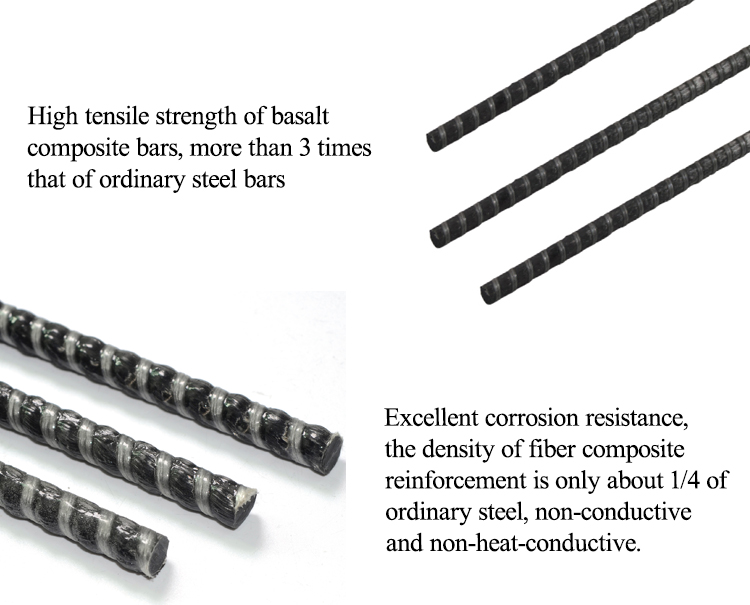
Basalt fiber is a new type of composite material combined with resin, filler, curing agent and other matrix, and formed by pultrusion process. Basalt fiber composite reinforcement (BFRP) is a new type of composite material made of basalt fiber as reinforcement material combined with resin, filler, curing agent and other matrix, and molded by pultrusion process. Unlike steel reinforcement, the density of basalt fiber reinforcement is 1.9-2.1g/cm3. basalt fiber reinforcement is a non-rusting electrical insulator with non-magnetic properties, especially with high resistance to acid and alkali. It has a high tolerance to the concentration of water in cement mortar and the penetration and diffusion of carbon dioxide, which prevents corrosion of concrete structures in harsh environments and thus serves to improve the durability of buildings.
Product Characteristics
Non-magnetic, electrically insulating, high strength, high modulus of elasticity, coefficient of thermal expansion similar to that of cement concrete. Very high chemical resistance, acid resistance, alkali resistance, salt resistance.
Basalt fiber composite tendon technical index
|
Brand |
Diameter(mm) | Tensile strength(MPa) | Modulus of elasticity(GPa) | Elongation(%) | Density(g/m3) | Magnetization rate(CGSM) |
| BH-3 | 3 | 900 | 55 | 2.6 | 1.9-2.1 |
< 5×10-7 |
| BH-6 | 6 | 830 | 55 | 2.6 | 1.9-2.1 | |
| BH-10 | 10 | 800 | 55 | 2.6 | 1.9-2.1 | |
| BH-25 | 25 | 800 | 55 | 2.6 |
1.9-2.1 |
Comparison of technical specifications of steel, glass fiber and basalt fiber composite reinforcement
|
Name |
Steel reinforcement | Steel reinforcement(FRP) | Basalt fiber composite tendon(BFRP) | |
| Tensile strength MPa | 500-700 | 500-750 | 600-1500 | |
| Yield strength MPa | 280-420 | None | 600-800 | |
| Compressive strength MPa | - | - | 450-550 | |
| Tensile modulus of elasticity GPa | 200 | 41-55 | 50-65 | |
| Thermal expansion coefficient×10-6/℃ | Vertical | 11.7 | 6-10 | 9-12 |
| Horizontal | 11.7 | 21-23 |
21-22 |
|
Application
Earthquake observation stations, harbor terminal protection works and buildings, subway stations, bridges, non-magnetic or electromagnetic concrete buildings, prestressed concrete highways, anticorrosive chemicals, ground panels, chemical storage tanks, underground works, foundations for magnetic resonance imaging facilities, communication buildings, electronic equipment plants, nuclear fusion buildings, concrete slabs for guideways of magnetically levitated railroads, telecommunication transmission towers, TV station supports, fiber optic cable reinforcement cores.